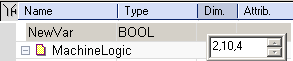
Create Variables
-
-
It is recommended to use the initial to reflect the variable type (e.g., Boolean with b; long integer with L) as a naming convention for variables.
Use the Dictionary
For explanations on dictionary usage, including how to create and Rename Variables see click here....
Create Variables from the Editors
Create
FBD editor
- Click the dedicated button
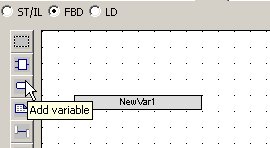
- Click a location in the editor (or double-click the variable if it is already created).
- Edit the name in the Variable Editor (or select an existing variable within the list which is already filtered according to their relevant data type).
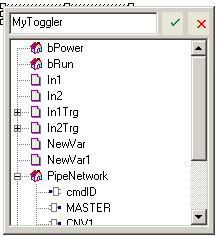
- The KAS-IDE automatically checks if the variable already exists. If it is new, you have to:
- Select its type in the drop-down menu: for FBD and FFLD, it is set by default according to the In or Out data type of the function block
- Specify where it is defined: the default is the current PLC program, but you can choose to make the variable Global or declared as a retain variable
Figure 1: Add Variable in FBD Editor
Figure 2: Define Variable Name in FBD Editor
Figure 3: Define Variable Type in FBD Editor
See FBD Variables for more information.
FFLD editor
- Double-click the in or out pins of the function block
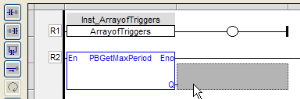
- Edit the name (or select an existing variable within the list which is already filtered according to their relevant data type)
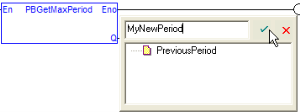
- The KAS-IDE automatically checks if the variable already exists. If it is new, you have to:
Figure 4: Add a Variable in the FFLD Editor
Figure 5: Define a Variable Name in the FFLD Editor
Data Types
You can create a variable of available Data Types.
For a list of types, click here...
Complex Structures
Complex variables are arrays, structures, and instances of function blocks. The following features are allowed for programming:
- Use arrays of structures
- Use arrays of FB instances
- Pass any complex data (array, structure, instance) to a UDFB or sub-program
There is almost no limitation in the amount of complex data declared (theoretically up to 4GB, but practically limited by the memory available in the runtime)
For more explanations on the Structure concept, refer to (➜ # 1, Structure)
Declare the Structure
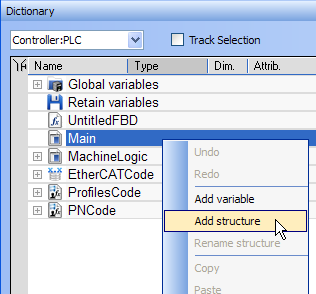
- Right-click in the Dictionary to open the menu.
- Select the Add structure command.
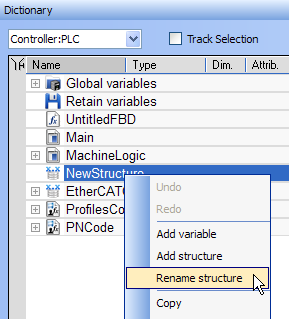
- Right-click on the new structure and select the Rename structure command.
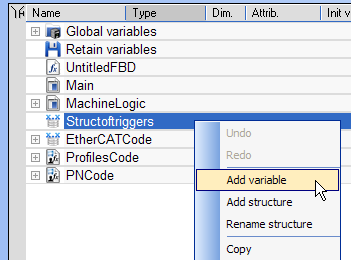
- Right-click on the new structure and select the Add variable command.
- Expand the new structure.
- Double-click on the new nested variable and define its name and type.
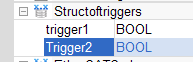
- Repeat steps 5 and 6 to add all the requested variables.
Create an Instance of the Structure
When finalized, drag-and-drop the structure from the library in the (Project) node to a program.
A new instance is automatically created.
- Select the new structure and move it with a drag-and-drop operation to the program declaration in the Dictionary.
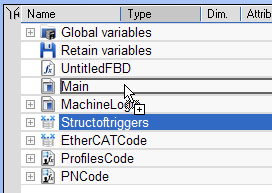
- You can also add a variable in the Dictionary with the Add variable command.
Then double-click on the new variable to define its type by selecting the structure type which is displayed in the Type drop-down menu.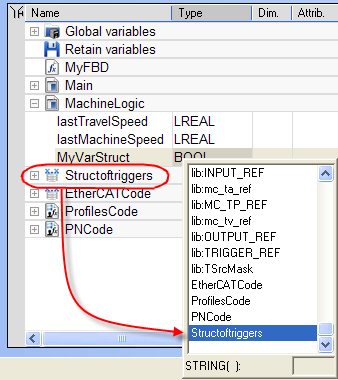
- Then you can drag this new instance and drop it in your program like any other variable
Figure 11: Create an Instance of the Structure